Today’s blog post provides two updates. First, an update on Windows 11 minimum system requirements based, in part, on feedback from the Windows Insider community. Second, information on the updated PC Health Check app that is now available to Windows Insiders.
Since the introduction of Windows 11, we have received valuable feedback from the Windows Insider community, our fans, customers and partners. Thank you for being a part of the release of Windows 11, coming at a time when the PC is playing a more central role in the way we connect, work, learn, create and play.
In June, we heard your questions about how we set the Windows 11 minimum system requirements and shared more information on the established principles that guided us in setting them. And as a team, we committed to exploring through Windows Insider testing and with OEMs whether there were devices running on Intel 7th Generation and AMD Zen 1 processors that met our principles.
Following the results of our testing, we are making a small number of additions to the compatible processor list (explained further below), but otherwise will maintain the minimum system requirements as originally set. We have concluded that the compatible 64-bit processors selected, 4GB of memory, 64GB of storage, UEFI secure boot, graphics requirements and TPM 2.0 are the right minimum system requirements to deliver on the principles we established to best support you.
We did identify a set of PC models that meet the principles while running on Intel 7th Gen processors that we did not originally include in our minimum system requirements. Based on those findings, we have expanded the list of compatible 64-bit processors to include the following:
- Intel® Core™ X-series, Xeon® W-series
- Intel® Core™ 7820HQ (only select devices that shipped with modern drivers based on Declarative, Componentized, Hardware Support Apps (DCH) design principles, including Surface Studio 2)
After carefully analyzing the first generation of AMD Zen processors in partnership with AMD, together we concluded that there are no additions to the supported CPU list. We will be updating the PC Health Check app to identify the correct systems with the newly added Intel CPUs in the coming weeks before the tool is released for general availability. Additionally, we will have more to share on the tools and reports IT Pros can use to understand their organization’s hardware eligibility at scale as we get closer to Windows 11 general availability later this year.
We have included more details below on our principles that guided us in establishing Windows 11 minimum system requirements. Here are some insights from the data we gathered over the last couple months that affirmed our decision.
- Reliability: Devices that do not meet the minimum system requirements had 52% more kernel mode crashes. Devices that do meet the minimum system requirements had a 99.8% crash free experience.
- Security: Windows 11 raises the baseline of Windows security by improving the security default configuration to combat increasing cyber-attacks. These requirements were informed based on trillions of signals from Microsoft’s threat intelligence as well as input from leading security experts like the NSA, UK National Cyber Security Center and Canadian Centre for Cyber Security. Additional details on the background and value of Windows 11 baseline are below.
- Compatibility: People continue to increasingly use their PCs for video conferencing, productivity and gaming. To ensure all Windows 11 devices can run a core set of applications to meet those needs, we set the minimum system requirements to align with some of the most commonly used apps.
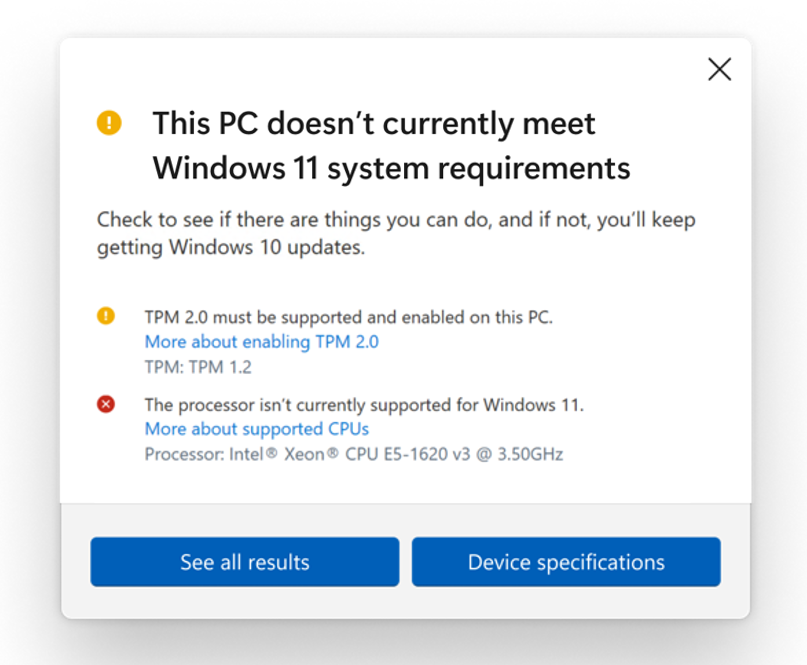
Following our announcement in June, we acknowledged that we missed an opportunity to provide clarity and accuracy through the PC Health Check app. Today, we are releasing an updated preview version of the PC Health Check app to Windows Insiders. This updated version expands the eligibility check functionality with more complete and improved messaging on eligibility and links to relevant support articles that include potential remediation steps – the screenshot below illustrates this. After a feedback period with Windows Insiders and with the additional updates for the newly added processors, we plan to re-release the PC Health Check app for general availability in the coming weeks. Today, we are also simultaneously releasing versions that support 64-bit Windows, 32-bit Windows, Windows on Arm and Windows 10 in S mode PCs to Windows Insiders. Windows Insiders can provide feedback on the PC Health Check app by going to Feedback Hub > Apps > PC Health Check.
As our unprecedented number of Windows Insiders have shown, most people with eligible devices will choose to move to Windows 11 to experience all the new innovations across connection, productivity, creativity and play that it has to offer. For those who are using a PC that won’t upgrade, and who aren’t ready to transition to a new device, Windows 10 is the right choice. We will support Windows 10 through October 14, 2025 and we recently announced that the next feature update to Windows 10 is coming later this year. Whatever you decide, we are committed to supporting you and offering choice in your computing journey. If you want to see the full Windows 11 minimum system requirements, you can visit this page.
Here is some additional detail on the principles that guided Windows 11 minimum system requirements:
- Reliability. Maintaining reliability over time is highly correlated with OEM and IHV driver support. The processors supported on Windows 11 are within OEM and IHV support and use modern (DCH) drivers. The move to modern drivers enables drivers and associated software to be installed and serviced in a coordinated manner through Windows Update and provides better mechanisms for tracking driver health. The result of this coordination is that system drivers are properly installed and functional after updates, providing a reliable experience when upgraded to Windows 11. From Windows Insider machines, those that did not meet the minimum system requirements had 52% more kernel mode crashes (blue screens) than those that did meet the requirements. Machines that met the requirements provided a 99.8% crash-free experience that is effectively managed by OEMs and IHVs through modern driver update management. Additionally, on unsupported hardware app hangs are 17% more likely and for first-party apps we see 43% more crashes.
-
Security: Windows 11 has raised the security baseline to make it the most secure version of Windows ever. We have used the more than 8.2 trillion signals from Microsoft’s threat intelligence, reverse engineering on attacks as well as input from leading experts like the NSA, UK National Cyber Security Center and Canadian Centre for Cyber Security to design a security baseline in Windows 11 that addresses increasing threats that software alone cannot tackle. We have carefully designed the hardware requirements and default security features based on an analysis of the most effective defenses. This analysis was based on the Microsoft data set of blocked attacks in 2020 which included 30 billion email threats, six billion threats to endpoint devices and 30 billion authentications. In addition to benefitting from these intelligence sources, Windows 11 enables proven security controls based on industry wide recommendations from global experts like the NSA and NCSC.
- The Trusted Platform Module(TPM) requirement enables Windows 11 to be a true Passwordless operating system, addressing phishing and other password-based attacks that are easier for attackers to execute when the TPM is not present. In the FY20 Microsoft digital defense report, Microsoft identified 67% fewer compromises of organizations that disabled legacy authentication and moved towards Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)- or Passwordless-based systems like Windows Hello. With Hello, the TPM works together with a PIN or biometric camera/fingerprint reader to securely store a secret in hardware that replaces a user’s password during authentication and is much harder to steal or spoof. The TPM is also used for numerous other Windows 11 features such as Bitlocker and Device Encryption, which leverages the TPM to store disk encryption keys. Research from Forrester showed that the loss or theft of assets like smartphones and laptops were involved in 20% of the breaches reported by global security decision-makers in 2020. Bitlocker full disk encryption in Windows 11 limits the possibility of sensitive data loss from lost or stolen devices. The TPM is also used to “bind” web-based credentials securely to a machine, preventing extraction and theft of credential types seen in many recent breaches. Windows 11 requires TPM 2.0 vs 1.2 because of the security advantages it provides, particularly support for newer and stronger cryptographic algorithms.
- The UEFI Secure Boot requirement ensures that a system boots with only code signed by either the device builder, the silicon vendor, or Microsoft. It does this by ensuring all code is signed by specific entities and by recording cryptographic hashes in hardware that can also be sent to the cloud to verify integrity. If a system can be compromised prior to the operating system boot, then all kernel, user and endpoint security tools can be completely undermined. The “NotPetya” attack, which cost hundreds of millions in damages, leveraged legacy bios to inject ransomware code before boot, which can now be mitigated by Secure Boot. The value and best practices of Secure Boot have also been validated by the U.S. National Security Agency. We have been requiring OEMs to ship using UEFI Secure Boot enabled since June 26, 2013 and want all Windows 11 devices to be able to provide that customer benefit.
- In addition to increased reliability, the supported processors increase security capabilities at the chip level. These processors provide virtualization extensions and virtualization performance improvements. Windows 11 supports virtualization-based security (VBS) which enables several security capabilities, including memory integrity, also known as hypervisor-protected code integrity (HVCI). HVCI disables dynamic code injection into the Windows kernel. HVCI also provides driver control and ensures that all drivers loaded meet a policy of allowed drivers set by Microsoft and the user. VBS also enables credential protection for common enterprise credential types (such as NTLM) an attack technique seen in “pass-the-hash” style attacks, and is the basis for System Guard Runtime attestation, a zero-trust capability that provides tamper proof hardware-based health statements to the cloud as part of a chip-to-cloud zero trust approach. The United States Department of Defense (DoD) requires virtualization-based security on Windows 10 for their devices. While we are not requiring VBS when upgrading to Windows 11, we believe the security benefits it offers are so important that we wanted the minimum system requirements to ensure that every PC running Windows 11 can meet the same security the DoD relies on. In partnership with our OEM and silicon partners, we will be enabling VBS and HVCI on most new PCs over this next year. And we will continue to seek opportunities to expand VBS across more systems over time.
- Compatibility. Windows 11 continues our strong commitment to compatibility. This means that devices can upgrade to Windows 11 and critical apps and devices will simply work. Raising the Windows 11 minimum system requirements enables us to better support apps and hardware for drivers and devices. Feedback also shows us that unsupported hardware is more likely to have older drivers that are incompatible with new OS features such as VBS. Supported hardware also comes with modern drivers, which helps ensure not only the reliability we mentioned earlier, but also great hardware compatibility. In addition, the new minimum system requirements establish a new baseline that aligns with the hardware needs of many of the most commonly used apps customers rely on today for teleconferencing, browsing, productivity and entertainment. Of course, certain features, apps, games and peripherals may have their own requirements that exceed our minimum system requirements so we encourage people who are buying new PCs to verify the requirements with the manufacturer of the specific products they will want to use.
Source: Windows Blog
—