The web’s success is due, in big parts, to its ability to support text entry and form submissions. In other words, entering text on webpages is a fundamental part of the web, which we’ve all used.
But today’s modern web applications go even further and let you edit entire documents, spreadsheets, or presentations. Other applications let you write code, chat with friends, or write emails.
Even though the use cases are very diverse, the underlying technology hasn’t changed much since the early days of the web. the HTML input and textarea elements are still the primary ways to enter text, and they work great. For more advanced use cases, web developers often rely on the contenteditable HTML attribute, which lets you capture rich text input.
These text editing primitives are powerful, but building advanced experiences still comes with a lot of challenges and sometimes requires less than ideal workarounds.
On the Microsoft Edge team, we’re very familiar with these challenges and work hand in hand with our partners to make text editing on the web a better experience for everyone.
In this article, we’ll share a few important improvements that we’ve recently made to Microsoft Edge and to the web platform, which we’re very excited about:
- Rewriting text with AI.
- Writing with digital pens directly on web pages.
- Building text editors that support advanced text-editing surfaces.
- Improving clipboard access APIs.
- And controlling text prediction features.
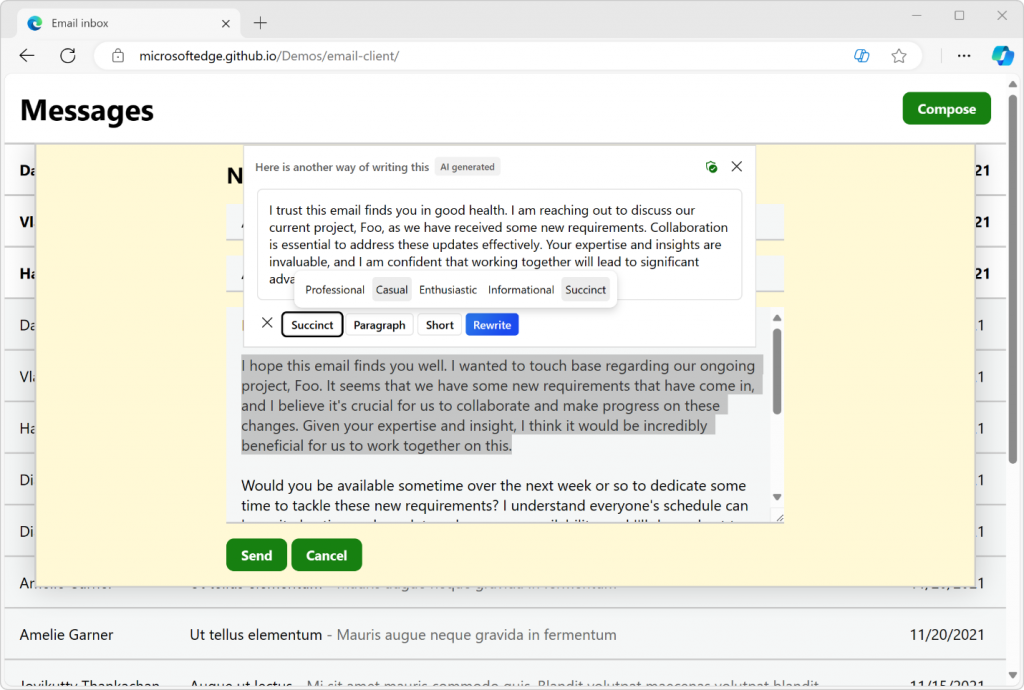
Rewrite text with Copilot
Starting with version 124, Microsoft Edge’s AI Compose feature becomes available inline, within editable text areas of a document.
Select a section of text that’s displayed in an editable field and click the Copilot icon to start rewriting that section, by iterating through different AI-generated proposals.
You can change the tone, format, or length settings to your needs.
Being able to access Copilot directly within input fields can save time and avoid context switching. But we also realize that not all text editable surfaces on the web need this capability, so we’re also introducing the writingsuggestions HTML attribute to disable it. More on this attribute at the end of this article.
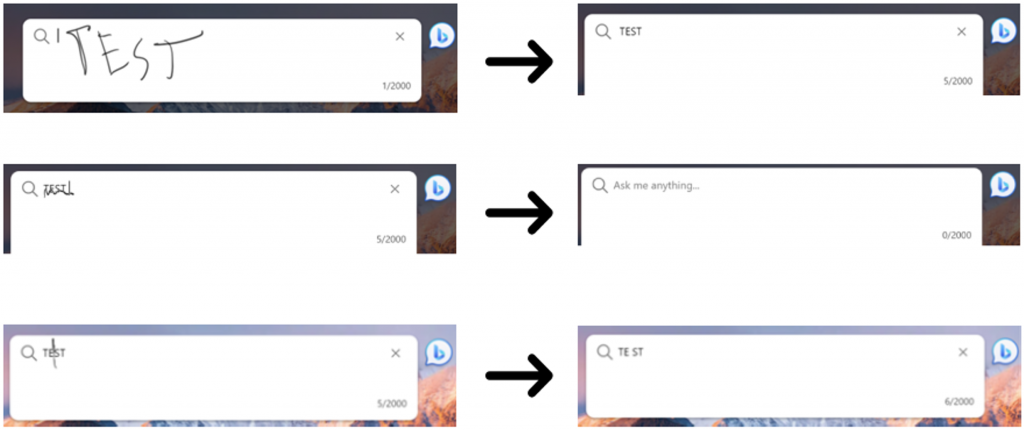
Write in any text field with a digital pen
Windows Ink allows you to write with a digital pen directly into an input field on Windows touch devices. This helps you stay in your workflow by reducing the need to switch back and forth between your keyboard and digital pen.
Microsoft Edge now also supports Windows Ink in places such as textarea elements, input elements, elements with the contenteditable attribute, or the browser address bar.
With Windows Ink support in Microsoft Edge, you can:
- Enter text by writing with a pen in, or near an input field.
- Delete text by scribbling over words to delete them.
- Add or remove spaces by drawing vertical lines in the text.
- Add line breaks by drawing horizontal lines.
Windows Ink can save a lot of time when interacting with webpages with a digital pen, and we would love to hear what you think and how we can improve the feature.
Note that you can toggle the feature in Microsoft Edge by going to edge://settings/content/HandwritingToText in a browser window.
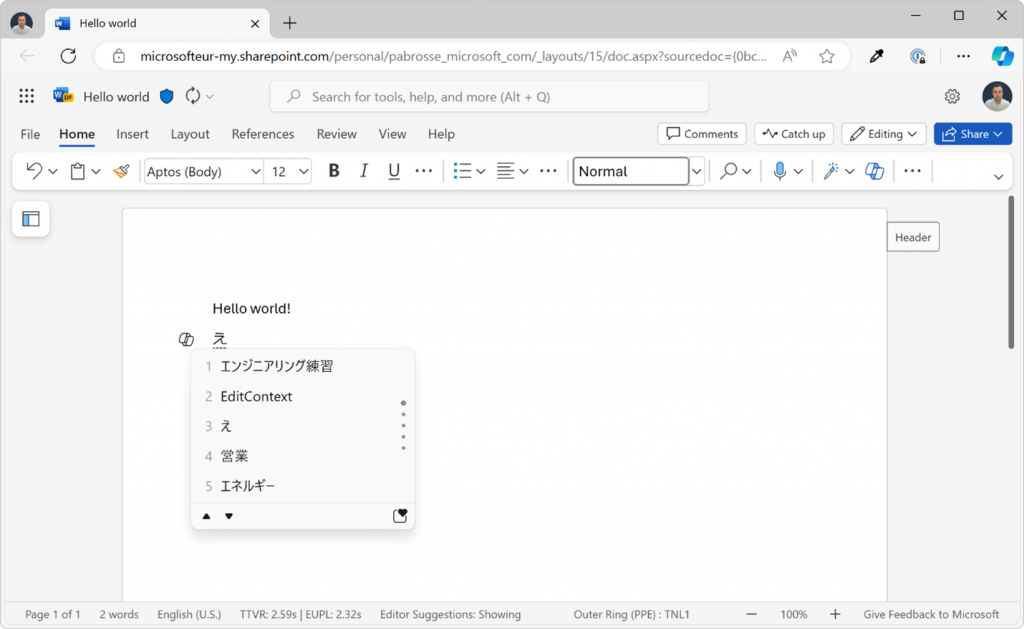
Build rich text editors that support advanced input methods
Today’s text editing techniques on the web make it hard to truly decouple the text input logic from the text rendering logic. Custom text editors often must use a hidden element that uses the contenteditable attribute to capture text input events, and then render the text separately, which often comes with accessibility issues.
To help with this, we shipped the EditContext API in Chromium to make it possible to create custom web text editors that support advanced input methods and avoid hacky solutions. The API is available in Microsoft Edge starting with 121, and in other Chromium-based browsers.
With the EditContext API, web developers can receive text input events directly through the API surface, which removes unnecessary complexity in the code, enhances accessibility, and lets developers create their own custom view of the edited text. For example, you can use the API to render the edited text in a <canvas> element if you want.
The API supports text-editing UI surfaces that a user might be composing text with at the operating system level, such as IME composition dialogs. It even supports Windows Ink.
To learn more about the EditContext API, check out our previous announcement, and the API’s reference documentation on MDN.
Copy & paste HTML
Text editing webapps often encounter clipboard issues when copying and pasting HTML formatted content. Sometimes, the format is lost, other times, the clipboard payload is much more complicated than it should.
To address this, we introduced the unsanitized option to the navigator.clipboard.read() method, allowing web applications to choose when they want to receive the full HTML content, rather than a browser-sanitized version of the HTML.
To learn more about how to use the option, check out the Clipboard read() method documentation on MDN.
This API has already helped us improve Excel Online by addressing several top copy-paste issues affecting the app. We shipped the API in Chromium, making it available to all Chromium-based browsers, including Microsoft Edge starting with version 122.
Detect supported clipboard formats
When writing data to the system clipboard, by using the Clipboard API, web developers have no way of knowing if the data they’re trying to write is supported. This means that they must first attempt to write the data to the clipboard and then check whether the write operation failed due to an unsupported data format.
This leads to more complex code and unnecessary cost in terms of CPU cycles.
To fix this, we’ve added a new static method to the ClipboardItem interface called supports(), which makes it possible to detect supported clipboard formats before attempting to write data. For example, to test if the text/html mime-type is supported, use ClipboardItem.supports("text/html").
This new method shipped with Microsoft Edge 121, and is available in other Chromium browsers too.
Control the browser’s text prediction feature
As mentioned before, Microsoft Edge lets you rewrite text with the inline Compose feature. Edge can also predict text as you type, with the text prediction feature. Text prediction makes writing much faster by completing sentences.
However, we realize that not all text editing surfaces on the web want the text prediction or inline Compose features available at all times. So, starting with version 124, we’re introducing a new HTML attribute called writingsuggestions. The new attribute can be used to turn off text prediction and inline Compose on any editor element. To learn more, check out our explainer document, and the attribute’s specification.
The new writingsuggestions attribute is now part of the Chromium codebase, making it available to all Chromium-based browsers. However, because Microsoft Edge is currently the only browser to have access to these text prediction and rewriting features, the attribute doesn’t have any effect in other browsers.
Text editing on the web is more important than ever, and we can continue making the user and developer experience better with new APIs and browser features that address specific challenges. We hope the improvements described in this article are useful to you.
As always, we’d love to know what you think or if you spot any issues! To reach out, click the … button in the top-right corner of Microsoft Edge, and then go to Help and feedback > Send feedback.
Source: Windows Blog
—